Introduction
This project will analyze molecular mechanism and functional effects of the the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS) and kallikrein-kinin system (KKS) in hypertensive cardiac damage. Our research program in this project is carried out in three complementary topics.
Topic 1:
Role of circulating and local aldosterone in hypertensive cardiac damage.
In double transgenic rat overexpressing the human renin and angiotensionogen genes (dTGR) we successfully performed gene expression profiling analysis in the heart and CD4+ cells by using microarrays. In the past, we performed two studies examining the role of the mineralocorticoid receptor in this model (Mazak et al. 2004) and treated dTGR with spironolactone and eplerenone. Both MR blockers ameliorated renal and cardiac damage (Fig 1).
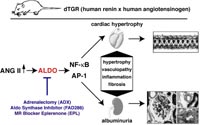
Project Status We recently performed several studies in dTGR rats study to elucidate the role of aldosterone signaling in cardiac and renal damage (Fiebeler et al. 2005;
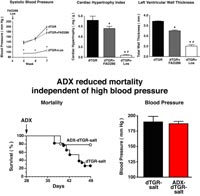
Fig 2, Pilz et al. 2005, Shagdarsuren et al. 2005), and determined gene expression pattern in dTGR rats developing cachexia and end-stage heart failure (Wellner et al. 2005). Our array experiments demonstrated that mitochondrial respiratory chain genes and lipid catabolism genes were reduced in expression while genes encoding transcription factors (CEBP-beta, c-fos, Fra-1), coagulation, remodeling/repair components (HSP70, HSP27, heme oxygenase), immune system (complement components, IL-6), and metabolic pathway were differentially expressed. Treating dTGR with losartan altered the gene expression patterns to those observed in Sprague-Dawley control rats.
Outlook We now started to analyze rats after myocardial infarction treated with an aldosynthase inhibitor and after adrenalectomy.
Lit.: 1. Mazak I et al. Aldosterone potentiates angiotensin II-induced signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation 2004;109:2792-2800. 2. Wellner M et al. Cardiac Gene Expression Profile in Rats with Terminal Heart Failure and Cachexia. Physiol Genomics. 2005;18:256-67. 3. Fiebeler A et al. An aldosterone synthase inhibitor ameliorates angiotensin II-induced organ damage. Circulation 2005;111:3087-94. 4. Pilz B et al. Aliskiren, a human renin inhibitor, ameliorates cardiac and renal damage in double transgenic rats. Hypertension 2005;46:569-76. 5. Shagdarsuren, E et al. Complement activation in angiotensin II-induced organ damage. Circ Res 2005 (in press).
Topic 2:
Cardioprotective mechanisms of kinins in transgenic rats.
We have established a transgenic rat model overexpressing tissue kallikrein mainly in the heart and have shown that these animals are protected from cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis caused by pressure overload, ischemia and diabetes (Pinto et al. 2000, Tschöpe et al. 2004a, 2004b, 2005).
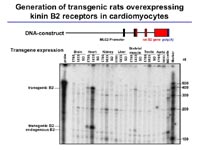
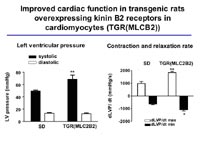
Project Status In order to further clarify the mechanisms involved in the cardioprotective effects of the KKS, we have generated a transgenic rat model overexpressing the kinin B2 receptor predominantly on cardiomyocytes (Fig 3).
These animals show a boosted response to bradykinin in Langendorff heart preparations, an improved cardiac function, and are protected from diabetes-induced LVH (Fig 4, Bader et al., unpublished).
We started to induce LVH and cardiac fibrosis in these rats after experimental pressure and volume overload initiated by aortic banding and aortocaval shunt, respectively. In order to induce hypertensive heart disease, the animals are currently crossbred with hypertensive TGR(mREN2)27 rats.
Outlook In double transgenic rats, blood pressure will be determined by telemetry and LVH and fibrosis will be analyzed by echocardiography, morphology and gene expression analysis. Alterations in the cardiac gene expression profile by the transgenic overexpression of the B2 receptor will be determined by microarray expression analysis in untreated TGR(MLCB2) rats and in animals after LVH induction in order to identify downstream effectors of the KKS in cardioprotection.
Lit.: 1. Pinto YM et al., Increased kallikrein expression protects against cardiac ischemia. FASEB J. 2000;14, 1861-1863. 2. Tschöpe C et al, Improvement of defective sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transport in diabetic heart of transgenic rats expressing the human kallikrein-1 gene. FASEB J. 2004a;18,1967-1969. 3. Tschöpe C et al., Prevention of cardiac fibrosis and left ventricular dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats by transgenic expression of the human tissue kallikrein gene. FASEB J. 2004b;18, 828-835 4. Tschöpe C et al., Inhibition of intramyocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy by transgenic activation of the kallikrein-kinin system. FASEB J. 2005, in press.
Topic 3:
Physiological genomics of blood pressure variability on cardiac damage in renovascular hypertension.
We showed previously that BPO markedly enhance sodium excretion and induce a frequency dependent deactivation of the renin system in freely moving animals (Nafz et al. 2000). This antihypertensive effect is mostly due to changes in plasma renin activity, renal renin mRNA content, renin protein content and particularly in changes of the renal protein/mRNA relationship. The latter suggests that translational mechanisms play a major role in BPO-dependent deactivation of the renin system and, therefore, in renovascular hypertension related end organ damage.
Project Status We also demonstrated that specific cellular proteins interact with the 3’-UTR of the renin mRNA, thereby, establishing a pathway to regulate renin synthesis in vitro.
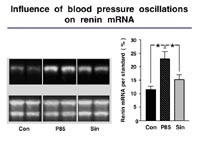
We now started to determine to which extend BPO (1) modulate cardiac renin handling, a major determinant of cardiac hypertrophy and contractile dysfunction, (2) promote cardiac vasculogenesis (Wagner et al. 2002) and (3) influence/ induce changes in specific cardiac target genes which are differentially expressed in response to BPO. The techniques of controlled induction of transient ischemia, BPO and different grades of renovascular hypertension in freely moving rats and mice are established.
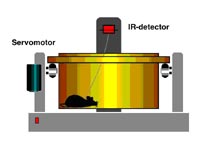
Outlook We started to investigate and to validate the relationship between novel candidate genes of cardiac end organ damage, BPO and specific forms of renovascular hypertension.
Lit.: 1. Wagner KD et al. The Wilms' tumor suppressor Wt1 is expressed in the coronary vasculature after myocardial infarction. FASEB J. 2002;16(9):1117-9. 2. Nafz B et al. Antihypertensive effect of 0.1-Hz blood pressure oscillations to the kidney. Circulation. 2000;101(5):553-7.